ミアシャイマー教授「米国の大いなる妄想」講演フル アメリカの失敗の数々 ※伊藤貫氏や中野剛志氏もたびたび引用する国際政治学者
Summary
TLDRこのビデオスクリプトでは、冷战後のアメリカの外交政策である「リベラルヘゲモニー」について批判的に分析しています。その戦略の失敗を指摘し、国家主義とリベラル主義の関係を解説します。さらに、アメリカが世界に植え付けようとしていた民主主義の価値観が、他国ではどう受け止められていたかについても触れています。また、中国の台頭とロシアの復興という新たな国際情勢下で、リベラルヘゲモニーが終焉を告げつつあると主張しています。
Takeaways
- 🌍 アメリカは冷战结束后,以自由霸权主义政策为目标,试图按照美国的形象重塑世界,但这一政策自2001年以来遭遇了连续的失败。
- 🤔 冷战结束后的乐观情绪和对自由主义的信仰导致了对世界改造能力的过分自信,但现实中自由主义与民族主义和现实主义的冲突导致了失败。
- 🇺🇸 自由主义是美国的核心意识形态,它基于个人主义,强调个体权利和社会契约,而民族主义则强调群体忠诚和国家主权。
- 📚 自由主义的两个基石是个体主义和对普遍原则达成共识的局限性,而民族主义则认为人类是社会动物,重视群体身份和国家主权。
- 🏛️ 自由霸权主义的三个组成部分是:全球推广自由民主、整合更多国家进入开放的国际经济体系、以及将更多国家纳入国际机构。
- 🔄 特朗普总统的外交政策反对自由霸权主义,他批评共和党和民主党的外交政策,并主张与独裁者建立良好关系。
- 💡 自由霸权主义的支持者认为,通过推广自由民主可以消除严重的人权侵犯,实现民主和平理论,并且保护自由民主免受内部威胁。
- 🔍 美国的自由霸权主义政策在中东、俄罗斯和中国等地区遭遇了失败,这些失败揭示了民族主义和现实主义对自由主义政策的抵制。
- 🛑 民族主义的力量是强大的,它强调自我决定和主权,这与自由主义推广个体权利的理念相冲突,导致在国际政治中的失败。
- 🛠️ 现实主义认为,在多极世界中,自由霸权主义不再适用,美国需要关注大国政治,特别是中国的崛起和俄罗斯力量的复兴。
- 🏠 自由主义在国外的推广可能导致国内自由主义的侵蚀,长期的战争状态可能导致国家安全状态的建立,影响国内公民自由。
Q & A
冷戦終結後のアメリカの対外政策の名称は何ですか?
-リベラル・ヘゲモニーと呼ばれ、アメリカの価値観を世界に広めることを目指した政策です。
リベラル・ヘゲモニーの主要な目的は何でしたか?
-アメリカのイメージに基づいて世界を再構築することが主要な目的でした。
リベラル・ヘゲモニーの失敗の主な理由は何ですか?
-ナショナリズムとリアリズムがリベラリズムに対して常に勝利するためです。
リベラリズムの基礎となる二つの前提は何ですか?
-一つは個人主義であり、もう一つは根本的な善の問題について普遍的な合意を得ることができないということです。
ナショナリズムの基本的な考え方は何ですか?
-人間は社会的な動物であり、部族に属しており、各部族が独自の国家を持つべきだという考え方です。
リベラル・ヘゲモニーの三つの主要な目標は何ですか?
-自由民主主義の普及、開かれた国際経済への統合、そして国際機関への統合です。
ドナルド・トランプはリベラル・ヘゲモニーに対してどのような立場を取っていましたか?
-トランプはリベラル・ヘゲモニーに反対し、自由民主主義の普及、開かれた国際経済、国際機関への統合に反対しました。
リベラル・ヘゲモニーの失敗の一例を挙げてください。
-中東における失敗が一例であり、アフガニスタンやイラクでの紛争が含まれます。
ナショナリズムがリベラリズムに勝る理由は何ですか?
-ナショナリズムは自己決定権と主権を重視し、外部からの干渉を嫌うためです。
講演者が提案する賢明な対外政策は何ですか?
-抑制政策を提案し、自由民主主義の普及をやめ、バランス・オブ・パワーの維持に集中することです。
Outlines
😐 リベラルヘゲモニーの失敗
コルドバ戦後のアメリカは世界をアメリカのイメージに再造するというリベラルヘゲモニー政策を追求したが、2001年以降の外交政策は失敗に終わっている。ナショナリズムとリアリズムがアメリカのリベラルな外交政策を常に打ち破っていると主張する。
🤔 リベラル主義とナショナリズムの基礎
アメリカは個人主義を重んじるリベラルな国として成立し、憲法や人権宣言はその思想を根底に置いている。一方、ナショナリズムは人々が部族社会に属する社会的な動物であると仮定し、個々人が国家を形成するのではなく、国家が個々のアイデンティティを形づけると説く。
🏛️ 国家主義とリベラル主義の違い
ナショナリズムは社会動物である人間の集まりである国家を重視し、主権や自己決定を重要視する。これに対して、リベラル主義は個人主義に基づく思想であり、個々人が社会契約を形成する。国家は個人を保護し、個々の自由を守る「夜間警備員」として機能する。
🌏 リベラルヘゲモニーの3要素
アメリカは世界中の国々をリベラル民主主義に変えることを目指し、国際経済への参加を促進し、国際機関への加盟を増やすことで世界をアメリカのイメージに再編するリベラルヘゲモニー政策を展開している。しかし、ドナルド・トランプはリベラルヘゲモニーに反対し、独裁者との親善や貿易保護主義を提唱している。
💡 リベラルヘゲモニーのメリット
リベラルヘゲモニーは人権侵害の排除、民主主義国家間の平和、国内での民主主義の安定化という3つの大きなメリットがあるとされる。しかし、アメリカの外交政策は失敗に終わり、特に中東地域での介入は多くの犠牲者を出してしまった。
🇺🇸 アメリカのナショナリズムと優越感
アメリカは非常にナショナリズム的な国であり、自己優越感に駆られ、世界をアメリカのイメージに変える力を持っていると信じている。このナショナリズムとリベラル主義の組み合わせは、アメリカが世界を変える力を持っていると信じる要因となった。
🕊️ リベラルヘゲモニーの限界
アメリカは冷战後、一極化世界の唯一の超大国としてリベラルヘゲモニーを追求したが、中国の台頭とロシアの復興により多極化世界へと移行している。この変化はリベラルヘゲモニーの終焉を意味し、大国間の力関係が主要な外交政策の議題になる。
📉 リベラルヘゲモニーの失敗
アメリカの外交政策は中東での介入、ウクライナ危機、中国との関係の悪化を通じて失敗に終わっている。ナショナリズムの力とリアリズムの現実主義は、アメリカが他国に政治制度を押し付ける試みを常に打ち破している。
🛡️ 国家主義とリアリズムの力
アメリカは軍事力で政权を転覆できる力を持っているが、その後の社会工学は大きな問題を引き起こす。イラクの事例から、国家の主権と自己決定の権利を尊重しなければ、他国に政治制度を押し付けることは困難であると示されている。
🏠 リベラル主義の国内での影響
永続的な戦争状態にあると、国内の自由主義に影響を及ぼす。国家安保保障の状態が成立すると、人々のプライバシーを侵害するスパイ活動を含む様々な問題が生じる。
🔄 一極化からの多極化への移行
アメリカは一極化世界から多極化世界へと移行している。中国の台頭とロシアの復興によって大きなパワーポリティクスが再び重要になる。この変化はリベラルヘゲモニーの終焉を意味し、アメリカは中国とロシアという同等の競争相手と直面している。
Mindmap
Keywords
💡冷戦後
💡リベラル・ヘゲモニー
💡ナショナリズム
💡リアリズム
💡リベラリズム
💡個人主義
💡主権
💡国際機関
💡ユニポラリティ
💡多極化
Highlights
The United States pursued a policy of liberal hegemony to remake the world in America's image after the Cold War.
Liberal hegemony has failed miserably, with significant foreign policy failures since the Cold War, especially post-2001.
The relationship between nationalism, realism, and liberalism is crucial to understanding these failures.
Liberalism in the John Lockean sense means the United States is a liberal democracy where both Republicans and Democrats are liberals.
Liberalism is fundamentally individualistic, emphasizing individual rights and the limitations of human critical faculties.
Nationalism is a powerful ideology that prioritizes group loyalty and social animals, often defeating liberalism.
Liberal hegemony attempts to spread liberal democracy, integrate countries into the open international economy, and promote international institutions.
Donald Trump opposed liberal hegemony, criticizing both Republican and Democratic foreign policies and rejecting spreading liberal democracy.
The failures of American foreign policy in the Middle East, NATO expansion, and engagement with China highlight the shortcomings of liberal hegemony.
Liberal hegemony fails due to the power of nationalism and realism, which emphasize sovereignty and self-determination.
The concept of liberal hegemony is based on a universalistic ideology that often oversells individual rights and misunderstands other cultures.
Nationalism emphasizes the importance of sovereignty, with nations wanting their own states and resisting external interference.
Liberalism abroad can lead to illiberalism at home, as a permanent state of war can undermine civil liberties.
The rise of China and the resurgence of Russian power signify the end of unipolarity and the transition to multipolarity, making liberal hegemony less feasible.
A policy of restraint, focusing on maintaining a favorable global balance of power, is advocated as a wiser foreign policy approach.
Transcripts
after the Cold War ended the United
States pursued a policy that I called
liberal hegemony
and the main aim of that strategy was to
remake the world in America's image
a policy has failed miserably if you
look at U.S foreign policy from the end
of the Cold War until now and especially
since 2001. it's marked by a whole
series of abject failures and I'll talk
about that at Great length and the sixty
four thousand dollar question is why why
was there all this optimism in the early
1990s why did people think we had the
wind at the back our back and we were
going to be able to remake the world in
our own image and today things
don't look good at all what went wrong
and my argument is that to understand
what went wrong you have to understand
the relationship between nationalism and
realism and liberalism and I believe
again that we have followed what is
essentially a liberal foreign policy
this is called liberal hegemony
and that it has been defeated at almost
every turn by nationalism and realism
okay now the way I want to proceed is
first of all I want to talk about what
liberalism is I don't want to talk about
what nationalism is and when I talk
about liberalism and nationalism I'm not
going to say anything about
International politics at least in any
meaningful way I just want to give you a
sense for what liberalism is the United
States is a thoroughly liberal country
it is a liberal democracy both
Republicans who we sometimes refer to as
conservatives are liberals and Democrats
are liberals I'm using the term liberal
in the John lockean sense of the term
the United States was born as a liberal
democracy the Declaration of
Independence the Constitution the Bill
of Rights these are thoroughly liberal
documents we are a liberal people
okay but what exactly does that mean
it's very important that you understand
it because you have to understand what
liberalism is to understand liberal
hegemony and what went wrong
then it's very important to understand
what nationalism is John's argument is
very simple here nationalism is the most
powerful ideology on the planet and in a
contest between liberalism and
nationalism nationalism wins every time
and what I want to do is explain to you
what liberalism is what nationalism is
and why nationalism defeats liberalism
then what I want to do is talk about
what liberal hegemony is what does it
mean to say that the United States is
interested in remaking the world in its
own image so I'll describe that I want
to talk about why we pursued liberal
hegemony and of course I've tipped you
off by telling you that the United
States is a thoroughly liberal country
but there's more to the story
then I want to tell you what our track
record is I want to describe our
failures in the Middle East with regard
to Nato expansion in Russia and with
regard to engagement in China let's talk
about
the evidence that we goofed
then I want to talk about why liberal
hegemony fails and this again is
basically a story about nationalism and
realism Trump being liberalism
and then I want to make the case for
restraint what I think is the wise
foreign policy okay
let me start
with what is liberalism
they're two Bedrock assumptions that
underpin liberalism
one is that it's individualistic at its
core
and number two is that there are real
limits to what we can do with our
critical faculties to reach agreement on
first principles or questions about the
good life
now what exactly am I saying
you
you have to decide when you think about
politics whether you think human beings
are first and foremost
individuals who form social contracts
you think that human beings are
fundamentally social animals who carve
out room for their individualism
this is very very important to think
about
right
liberalism is all about individualism
liberal theorists are known as social
contract theorists because they believe
that individuals come together and form
social contracts
so the focus is on the individual the
Assumption underpinning liberalism is
not that human beings are social animals
from the get-go
that's the first point
the second point is that liberalism
assumes that we cannot use our critical
faculties we cannot use reason to come
up with truth about first principles
think about issues like abortion
affirmative action you cannot get
Universal agreement on those issues
right and I'll talk about this more as
we go along but the roots of liberalism
are traced back in my opinion to the
religious wars in Britain between
Catholics and Protestants and the fact
is you cannot use your critical
faculties to determine whether
Catholicism is a superior religion to
protestantism or vice versa or whether
atheism is superior to both of them
where Judaism or islamist area to
Catholicism and protestantism who knows
right you just can't reach agreement
there are real limits
to what we can do with our critical
faculties okay so these are the two
Bedrock assumptions one you focus on the
individual
and number two you accept the fact that
you can't reach Universal agreement
now
central question how should politics be
arranged to deal with this potential for
violence and you say yourself what does
he mean potential for violence the fact
is that Catholics and Protestants were
killing each other in huge numbers not
only in Britain but all over Europe
people today she is in sunnis kill each
other because they can't agree on
whether she has a sonism is the correct
interpretation of Islam
Communists versus liberals people can't
agree on first principles and when they
can't agree on first principles if they
feel really strongly about them there is
potential for violence
so when you have all these individuals
running around
who
don't agree they may agree in some cases
but don't universally agree
there's tremendous potential for
violence
so liberalism is basically an ideology
that's based on conflict and the
question is how do you solve that
conflict
there's a three-part solution and this
should be dear to all of your hearts
the first is
you focus on individual rights remember
the importance of the individual
you know the Declaration of Independence
life liberty and the pursuit of
happiness
those are natural rights those are
inalienable rights this means that every
person on the planet has a particular
set of Rights
sometimes defined as freedoms
this is to say you if you want to be
Protestant have the right to practice
that religion and if I want to be a
Catholic I have the freedom I have the
right to be a Catholic
the name of the game is to recognize
that everybody has these freedoms to
choose
this makes perfect sense when you think
about Catholics killing Protestants
right or Jews killing Muslims or
whatever group you want atheists killing
believers
communist killing
whatever right the point is you want to
focus on the individual and let the
individual choose for him or herself
what kind of Life they want to lead you
want to let them lead as much as
possible their version of The Good Life
and very important every person on the
planet
has that right
and let me get ahead of myself here just
put this seed in your brain If you focus
on individualism and inalienable rights
you go almost automatically from an
individualistic ideology to a
universalistic ideology
right because again you're focusing on
the individual you're saying every
individual has a set of Rights every
individual on the planet that
individualistic
ideology becomes a universalistic
ideology
but we're talking about
the individual here the second is you
purvey the norm of Tolerance
we talk about tolerance all the time
universities are really big on tolerance
we're supposed to tolerate opinions that
we don't like
you bring in speakers or you allow
speakers to come in who say things that
you find reprehensible
right tolerance really matters
but the fact is the tolerance only takes
you so far because you're dealing with
people who sometimes are so committed to
their beliefs
you know somebody who believes that
abortion is murder is willing to murder
a Doctor Who practices abortion right so
you need a state that's the third
element of the equation you need a state
that's effectively a night Watchman that
makes sure that those people over there
who want to live as Protestants don't
attack those people who want to live as
Catholics or vice versa this is the
liberal solution this is what America is
all about
individualism we talk about it all the
time we talk about rights everybody has
rights my kids over the years have
always reminded me when I tell them that
they have to do X Y and Z that they have
rights
and I cannot interfere with their rights
right that's the way we're educated from
the get-go and of course we're a
remarkably tolerant people as societies
go not completely but that's of course
why we have a state
right you gotta have a police force
you've got to have a system of Courts
right so that's that's what liberalism
is all about right liberalism focuses on
the individual right pervades the norm
of Tolerance and accepts the fact that
you need a night Watchman State now
let's talk about nationalism
different animal
nationalism is based on the assumption
that human beings are social animals
we are born and we are heavily
socialized into tribes
we are not born in the state of nature
we are not individuals born and left
alone in the woods we are born into
groups we are very tribal
so you see in terms of starting
assumptions or Bedrock assumptions what
underpins nationalism what underpins
liberalism very very different
and individualism takes a back seat to
group loyalty
right
somebody around the world kills an
American
Isis kills an American it's
fundamentally different
than killing a Saudi or killing a Brit
because you're killing one of us
this is the tribe right you're an
American
Americans look out for other Americans
we're social animals from the get-go
and aside from the family the most
important group remember I said that
you're born into and heavily socialized
into particular groups putting aside the
family the most important group in
today's world
is the nation
I'll say more about that in a second
what's nationalism here's my simple
definition
it's a set of political beliefs
which holds
that a nation a nation a body of
individuals with characteristics that
purportedly distinguish them from other
groups should have their own state
think of the word nation state nation
state nation state embodies what
nationalism is all about it says the
world is divided up into these tribes
called Nations and each one of them
wants its own state
if you think about the world today just
look at a map of the world today it is
completely covered with nation states
nothing but nation states if you went
back to 1450 and you looked at a map of
Europe there isn't even a single state
on that map over time the growth of the
state and then the growth of the
nation-state
you move to a world that is filled with
nothing but nation states
look at the Palestinians and the
Israelis the Jews
who believed in Zionism
what is Zionism all about it's all about
having your own Jewish State Theodore
herzl who's the follower of Zionism his
most famous book is called the Jewish
State Jewish nation state what do the
Palestinians want two-state solution
Palestinians want their own State
Palestinians are Nation they want their
own state
the planet is filled with Nations many
of which have their own state
almost all of which want their own State
nation state right that's what
nationalism is all about
taking a step further
Nations Place enormous importance on
sovereignty
or self-determination
which is why they want their own State
the Palestinians don't want the Israelis
deciding
what their politics should look like
Palestinians want their own State Jews
want their own State Germans want their
own state
Americans want their own state
because they believe in sovereignty you
saw this with Donald Trump remember
Donald Trump ran in the campaign on a
platform that he referred to as America
first
just think about that America First
America
particular Nation
take care of us first and he has made it
very clear that he does not want anybody
interfering in our sovereignty and he
was saying yesterday he doesn't think we
should be interfering in the sovereignty
of other countries
right that's recognition of the power of
nationalism
so Nations
want their own State and then once you
get nation states they Place enormous
importance on sovereignty or
self-determination who are these
Russians to be interfering in our
elections the United States is a
sovereign country no country like Russia
or any other country for that matter has
the right to interfere in our elections
the basic argument here that's what
nationalism is really all about
okay so you get a feel for the
difference between liberalism and
nationalism liberalism focuses on the
individual
and therefore because it emphasizes
individual rights which everybody has
has a universalistic dimension
nationalism is particularistic at the
core
right fundamentally different
okay so what's liberal hegemony I've
given you the definition
of liberalism and the definition of
nationalism that I've worked out let me
talk a little bit about liberal hegemony
it's basically an attempt to remake the
world in America's image
it has three components
first is
spreading liberal democracy all over the
globe and the reason that I put three
stars
up there is it is the most important of
the three
this is the idea that we want to turn
every country into a liberal democracy
we want every country on the planet to
have the same political system that we
do here in the United States
second goal is we want to integrate more
and more countries into the open
International economy
this is where we have an emphasis on
free trade lots of economic intercourse
right free Capital flows and so forth
and so on you know the whole story
and then third is we want to integrate
more and more countries into
International institutions like the
World Trade Organization the IMF NATO
think NATO expansion the TPP
trans-pacific partnership which the
Obama Administration was building in
which president Trump
cashiered okay the liberal
story places a great emphasis on
institutions it places a great emphasis
on an open International economy and
most importantly on spreading democracy
just to give you a feel for this Donald
Trump ran against liberal hegemony
right and liberal hegemony to be clear
was supported by both Republicans and
Democrats as I like to say the
Republicans especially but the Democrats
also like to make the argument that
there's a big difference between the two
parties on foreign policy this is not a
serious argument this is Tweedledee and
Tweedledum hardly any difference between
the Republicans and the Democrats
there's a real difference between Donald
Trump and both of them remember Donald
Trump ran the table in the Republican
primaries by criticizing the Republicans
performance on the foreign policy front
for decades and criticizing the
Democrats in the general election Donald
Trump said I'm not interested in
spreading liberal democracy across the
globe and in fact he was quite
comfortable
making nice with dictators second he was
not interested in supporting an open
International economy in fact he is
showing today that he is willing to put
tariffs on China Canada and our European
allies and as far as International
institutions are concerned he said NATO
is obsolete he was
contemptuous of the World Trade
Organization contemptuous of the
European Union does not like the IMF
does not like the World Bank does not
like NAFTA cashiered the TPP that's
that's Donald Trump he ran against this
but Obama George W bush Bill Clinton
George H.W bush they embraced this after
the Cold War ended
and by the way it was the failure of
this policy it's the failure of American
policy that helped put Donald Trump in
the White House
for those of you who say to yourself how
could this man have ever been elected
president of the United States I'm
telling you an important part of the
story
right it's the failure of the foreign
policy Elites in this country
to produce over the past
30 years
okay
what are the benefits of liberal
hegemony this is very important
in other words why did we go down this
road in part is due to the fact that
foreign policy Elites in the United
States had a story to tell about how
this was going to lead to all sorts of
wonderful consequences first of all if
you turn every country on the planet
into a liberal democracy you basically
eliminate significant human rights
violations we don't need r2p or any more
of these policies that are designed to
run around the world protecting human
rights because human rights are no
longer threatened because the world is
comprised of nothing but liberal
democracies second and maybe even more
importantly
liberals tend to believe and again I'm
using liberals to include Democrats and
Republicans they believe in what's
called Democratic peace theory that is
that liberal democracies don't fight
each other so if you can create a world
of nothing but liberal democracies
they don't fight each other peace breaks
out
and problems like proliferation and
terrorism are taken off the table and
it's just the world peace love and dope
can't get much better than that right
and then finally it makes the world safe
for Liberal democracy as you all know
inside every liberal democracy there are
going to be elements who don't like
liberal democracy
when I was a kid this was the Communist
Party in the United States well if
there's no Soviet Union out there that's
a communist state that can interact with
those Communists in the United States
that you don't have to worry about those
Communists in the United States getting
support from abroad so what we do is we
make the whole planet
nothing but liberal democracies and that
really ameliorates the problems that any
of these liberal democracies have on the
home front because there's no foreign
power that can assist them this is a
Woodrow wilson-like argument made by the
likes of George Bush right so these are
the three great benefits of liberal
hegemony and this is what propelled
people to pursue this policy of remaking
the world in America's image which
mainly means spreading liberal democracy
now why did the U.S pursue liberal
hegemony
first of all as I said to you folks
before the United States is a profoundly
liberal country
it makes the United States a wonderful
place
you should understand here
that I am not arguing that liberalism is
a Bad Thing period end of story I
actually think that liberal democracy is
the best political system you can
possibly have and I thank my lucky stars
that I was born in the United States of
America a liberal democracy and raised
in a liberal democracy I would want it
no other way
my argument is that liberal democracy is
the best of all possible political
systems that you can have but as a
foreign policy
liberalism is bankrupt right so you
understand the argument I'm making here
but this is a fundamentally liberal
country and realists like me John
Schuster Jason Castillo they can tell
you this realists like me and them have
a tough time in America because liberals
don't like realists right that's why so
many people don't like me right because
I'm a realist on foreign policy grounds
right right so this is a profoundly
liberal country and just to go back to
that slide
when you start trying to sell these
kinds of arguments in the early 1990s
it's very easy to do
America is just gravitate to these
arguments because it is a liberal
country
second
American nationalism supplied an
unhealthy dose of hubris to the equation
this is a very important part of the
story
John told you that nationalism is the
most powerful political ideology on the
planet
what I'm telling you also I didn't say
this before I'm going to tell you now
the United States is a very
nationalistic country if you go to the
library here University of Chicago
Harvard you name it right there are
whole wings of the library that are
filled with books about American
liberalism
there is probably one shelf worth of
books on American nationalism because we
never talk about ourselves as a
nationalistic country we are very
nationalistic let me just say a few
words about this Madeleine Albright
canonical liberal right loves liberal
hegemony is famous for saying this
America is the indispensable Nation
we stand taller and we see further
this is pure unadulterated nationalism
America is America as opposed to the
other
right that America is the indispensable
there's the word Nation Nation as a
nationalism we we are the indispensable
Nation we stand taller and we see
further
we are superior you all know we're the
city on the hill right we have the right
we have the responsibility and we have
the capability to transform countries
all around the world into liberal
democracies
nationalism
so what I'm saying to you here
oh let me just give you another example
American exceptionalism you surely all
believe in American exceptionalism and
if any of you plan to run for political
office in the United States you better
say you believe in American
exceptionalism Andrew Cuomo just got
himself in trouble for denying that and
Barack Obama flirted with that argument
and he quickly backed off
well if you believe in American
exceptionalism you believe in American
nationalism because exceptionalism is
what nationalism is all about
so what you have here is a country
that is
fueled by both nationalism and
liberalism
right
so it is hardly surprising that this
country is going to go on a rampage and
try to remake the world
and then finally and this is a very
important part of my argument I believe
you can only pursue liberal hegemony in
unipolarity
the reason is if you're in bipolarity or
multi-polarity
you have other you have other great
powers to deal with and you have to act
according to the dictates of realism
right bipolarity means two great Powers
multi-polarity three or more unipolarity
there's only one great power well if
there's only one great power
you don't have to worry about great
parapolitics this is where the United
States was at the end of the Cold War we
were Godzilla
we were incredibly powerful relative to
everybody else in the system
tremendous amounts of power Charles
Krauthammer called this the unipolar
moment
so here we are we're incredibly powerful
and we think that liberal democracy is
the wave of the future we think we have
the wind in our back and we think the
idea of spreading liberal democracy
given how powerful we are it's going to
be easy and we don't have to worry about
balance of power politics 1991 the
Soviet Union disappears
it was a weak lean even before it
disappeared China hasn't risen yet
there's nobody else out there we have to
worry about the balance of power so we
are free to pursue liberal hegemony if
you're in a bipolar system or a
multi-polar system I'm getting way ahead
of myself now think rise of China think
resurrection of Russian power
not much room for Liberal hegemony
you're talking about balance of power
politics pivot to Asia dot dot dot you
know the story but here if you have
unipolarity and the sole pole that's
Uncle sugar the soul pole is profoundly
liberal right and profoundly
nationalistic you're Off to the Races
and that's what happened in starting in
the early 1990s
yeah liberal hegemities track record
just want to talk a little bit about
this these are the failures of American
foreign policy
talk about the Bush Doctrine and the
greater Middle East Afghanistan
you think we're going to turn
Afghanistan into a liberal democracy
just a question when we turn it back
over to the Taliban uh longest war in
American history
Iraq total disaster led to the creation
of Isis hundreds of thousands of people
died
uh
Iran now has significant influence in
Iraq
Syria we played a key role in unsettling
the regime in Syria that's worked out
really well
Libya we played a key role in toppling
Colonel Gaddafi power that's really
worked out very well we're deeply
involved in the war in Yemen now which
is a human rights catastrophe the
Americans ought to be embarrassed
for their disgraceful Behavior
supporting this war supporting the
Saudis
you look at our track record in the
greater Middle East failure after
failure and Donald Trump to his credit
pointed this out in the campaign and the
American people fully understand this
the Elites in this country don't because
they're deeply invested in these wars
but
disable track record uh the Ukraine
crisis and U.S Russia relations of
course
inside the elite we blame the Russians
the Americans never blame themselves for
anything but actually what happened here
is that the United States decided when
the Cold War ended that we would take
NATO and we would take the EU and we
would March them Eastward right up to
the border of Russia
and what we would do is we would help
solidify
the democracies that had emerged in
Eastern Europe after the Cold War we
would get the countries in Eastern
Europe embedded in international
institutions like NATO and the EU we
would get them hooked on capitalism and
we would make sure they were liberal
democracies by the way those countries
that weren't liberal democracies we
would foment revolutions remember the
orange revolution in Ukraine the rose
Revolution
in Georgia right it's a whole part of a
piece it's all part of this story
right realist like me George Cannon we
all said are you crazy you think you
could take a military Alliance that was
a mortal enemy of the Soviet Union
during the Cold War and March it right
up to the Russian's border and they're
just going to sit there and take it and
of course the Russians screamed buddy
murder about NATO expansion from 1995
forward
we didn't listen
right but it eventually blew up in our
face Georgia 2008 Ukraine 2014. we are
principally responsible for creating the
crisis that led to Russia recapturing
Crimea or capturing Crimea depending on
your view and for the war in Ukraine
today the Russians have basically said
you're not going to make Ukraine a
western bulwark on our border not going
to happen we'll wreck it before we let
that happen and they said the same thing
about Georgia from an American point of
view this makes Emily good sense you've
all heard of the Monroe Doctrine right
you know what the Monroe Doctrine says
no distant great power from Europe or
East Asia is allowed to come in to the
Western Hemisphere with military force
and form an alliance with any country in
this region
that's that's the Monroe Doctrine
I'm old enough to remember the Cuban
Missile Crisis we went ballistic when we
found out the Soviets had put missiles
in Cuba and then later they were talking
about building a naval base at Cien
fuegos who do these people think they
are don't they understand that this is
the Western Hemisphere they are not
allowed
to move military forces into this region
we still have sanctions on Cuba
God knows how many years since 1959 this
has been going on because the Cubans had
the audacity to form a military alliance
with a distant great power well as my
mother taught me when I was a little boy
what's good for the goose is good for
the gander if we can have a Monroe
Doctrine are you shocked that they had a
Monroe Doctrine or they have a Monroe
Doctrine you're shocked that the
Russians don't like the idea of us
marching NATO right up to their border
you shouldn't be
you shouldn't be great Powers I can tell
you from studying a lot of military
history are remarkably sensitive about
their borders and the idea that an enemy
is going to creep right up to their
borders and they're just going to stand
there and say oh that's okay
we live in a world of peace love and
dope that's not the way International
politics works that's realism 101
slamming liberal
hegemony it's also all about nationalism
right because the United States is
interested in interfering in the
politics of both Russia and China and
this brings us to engagement with China
our goal from the beginning has been to
turn China into a liberal democracy that
involves interfering with their politics
do you think they were happy about that
no they weren't
let's go back to the goose and the
gander you've been watching all these
Americans screaming bloody murder about
the fact the Russians are interfering in
our election well don't you think the
Chinese and the Russians are going to
scream bloody murder when we try and
interfere in their politics they are
surprise of surprises
but of course liberals and here I'm
again I'm talking about Republicans and
Democrats the U.S is a benign hegemon
we're benign hegemon we only have good
intentions and we just want to make the
world look like us and of course once
that happens we all live happily ever
after didn't work out that way just look
at that giant disaster Zone called the
Middle East look at the hundreds and
hundreds of thousands of people who've
died we have a lot of blood on our hands
U.S Russian relations we bear principle
responses the principal responsibility
for the deterioration of those relations
and with regard to engagement it's been
a failure
principal Architects like Kurt Campbell
now admit that's true we failed right
the policy has been an abject failure
so the question is why did it fail
I'm not going to go into this any detail
but
power of nationalism
right
I was one of the leading opponents there
weren't many uh
in the sort of foreign policy
establishment
I was one of the leading opponents of
the Iraq War I think it was because I
was in the American Military from 1965
to 1975 which was coterminous with the
Vietnam War and when I heard that these
people were thinking about invading Iraq
he said if they lost their mind right
there's no question the United States
military is an incredibly formidable
fighting force and we can topple regimes
almost anywhere in the world maybe China
and Russia left out we can go into Iran
go in Iraq go into Syrian topple regimes
but the problem is what do you do once
you own the place right what do you do
you agree that as a liberator the first
day week maybe even the first month
right all sorts of people were glad we
got rid of Saddam Hussein but then we
got to stay to do social engineering and
this is a prescription for big trouble
remember what I told you about
sovereignty remember what I told you
about self-determination you think the
Iraqis wanted us telling them what color
toilet paper they could use I don't
think they liked it at all and we had
resistance serious resistance
you want to wreck Russia tell them to
invade Ukraine that'll be pretty
let them go with the Latvia Lithuanian
Estonia let him re-establish the Soviet
Empire in Eastern Europe you think
that'll make them more powerful they'll
be up to their eyeballs and alligators
I remember in 1979 the Soviets invaded
Afghanistan virtually everybody in the
National Community security Community
was aghast oh my God the Soviets are on
the March this is the end of the world I
said you've got it all wrong they just
jumped into a giant tar pit
when you're involved in an arms race
with a country like the Soviet Union
what you want them to do is go in
Afghanistan just like you want us to go
into Vietnam you want to do that one
again
almost tore this country apart
almost wrecked our military
whoo
I told the Chinese when I first started
going there in the early 2000s but you
ought to tell the Americans you're
counting on them to win the war on
terror tell them they got to stay in
Afghanistan and Iraq until they win the
war they'll be there forever grinding up
their military wrecking their economy
you know what the lesson here is stay
out of those places unless you
absolutely have to go in but we had
exactly the opposite world view because
we had a foreign policy that's based on
liberalism
right we thought we had a right
responsibility and the capability to do
all the social engineering power of
nationalism you never want to
underestimate it and you want to
understand that as Americans you are
very nationalistic and you ain't special
everybody else on the planet is very
nationalistic and nationalism is all
about self-determination and sovereignty
and if you don't like people interfering
in your politics don't be surprised if
they don't like you interfering in their
politics
talk about the power of realism
again when you're dealing with China and
you're dealing with Russia you're
dealing with very powerful countries and
you start moving military alliances you
start moving military forces up to their
borders you get in their face you're
asking for serious trouble right just
talk to the Chinese sometime about how
they think about those American Naval
and Air Forces right off their Coast it
really bothers them they don't like it
at all I don't blame them
right as an American I'm glad we're
there I want to contain the Chinese well
you're very clear about that I'm a
realist
realist I I don't
want to cut the Chinese any slack
but I understand why they get upset
but again liberal hegemony doesn't by
that line of argument
now I want to talk about overselling
individual rights in a liberal
liberalism just very quickly on
overselling individual rights
the fact is that we make a really big
deal about the importance of Rights here
in the United States
but if you look around the world
most people don't really think that
individual rights matter that much and a
thoroughly liberal country like the
United States you can sell that kind of
argument up to a point
it's very hard to do abroad especially
in countries where people price security
if you go to Russia Today
and you talk to people about liberal
democracy and rights they will tell you
almost all of them we tried that in the
1990s and Russia was turned into the
wild west we're much happier with Putin
and the political system that we have
soft authoritarianism is much more
suited for us and we don't care that
much about rights we have some rights we
understand their limits but we don't
want your political system we've been
there we tried that it didn't work
so what I'm saying to you is in a lot of
countries
when you invade them and you think you
can do social engineering all for the
purpose of turning them into liberal
democracies what you discover in almost
all those cases is that being turned
into a liberal democracy where
individual rights are prized is not that
important it's not to say it's
unimportant but people are just not
craving for individual rights and in
many cases they're just craving for
stability if you're an Iraqi and it's
2003 and Uncle sugar pays you a visit he
topples the regime right and then chaos
breaks out over the next couple years
you're not going to be worried too much
about creating a liberal democracy
you're not going to be worried too much
about individual rights you're just
going to be worried about what you can
do to stabilize the country so that you
and your family don't get killed right
so you just want to understand that
we tend to oversell individual rights
and when you marry that with the power
of nationalism and the power of realism
you get into real trouble my final Point
has to do with the Liberal Liberal
illiberal liberalism
remember when I told you about
liberalism to begin with
I told you that liberalism was
predicated on the assumption that you
could not reach Universal agreement on
first principles remember I told you
that
and therefore you develop sort of a Live
and Let Live
political order that's what liberalism
is
it's a modus the vendai form of politics
you'll let people decide for themselves
if he wants to be a Protestant I want to
be a Catholic he wants to be a Jew I
want to be a Muslim you let people do
what they want
okay
because you can't reach Universal
agreement
if you you think about it liberal
hegemony
is based on intolerance it says
everybody has to be a liberal democracy
my view is if you have soft
authoritarianism in Russia so what
that's their choice
why can't they have a soft authoritarian
system why do we have to say everybody
has to look like us
isn't this antithetical to the basic
liberal Enterprise
I think the answer is yes
case for restraint very quickly
uh
if I'm running foreign policy
and you can rest assured that will never
happen but if I was running American
foreign policy from the early 90s
forward I would have pursued a policy of
restraint
uh I would have abandoned liberal
hegemony
uh
uh which mainly means abandoning the
policy of spreading democracy around the
world
okay I think that that was the key
mistake that we made
right we we thought that liberal
democracy was going to take root
everywhere
for those of you you young people who
haven't read Frank fukiama or Francis
fukuyama's famous article the end of
History you really should read it the
two most important articles that were
written when the Cold War ended were
Francis fukuyama is the end of history
and Charles krauthammers the unipolar
moment and basically what Frank fukuyama
said is that we spent the first half of
the 20th century defeating fascism we
spent the second half defeating
communism and now the
we had won those two battles all that
was really left standing was liberal
democracy and the world was slowly but
steadily going to evolve into a system
of liberal democracies and Frank says at
the very end of the piece that the
biggest problem that we're going to face
in the future is probably boredom
boredom why boredom because once you
have a world that's populated by all
liberal democracies you get peace
uh and Krauthammer wrote this piece
called the unit polar moment that he
said this is a unique moment in world
history in the United States is by far
the most powerful State on the planet we
have this tremendous military and we
ought to use it to reshape the world in
our own interest you marry krauthammers
argument with fukiyama's argument
fukuyama says we've got the wind at the
our back
Kraut Hammer says we have this big stick
that we can use to facilitate the
process and you're Off to the Races
right and this of course is exactly what
happens but I would have abandoned that
and I would have concentrated instead on
maintaining a favorable Global balance
of power
which mainly means containing the rise
of China right as you would expect from
a realist like me what I really care
about is not what kind of political
system a state has I just care how much
power it has and my principal goal as an
American is to make sure we are the most
powerful State on the planet
and as many of you know in my lexicon
that means to make sure we are hegemon
in the region in the Western Hemisphere
we want to be a regional hegemon on the
Western Hemisphere and make sure that
there is no hegemon in Europe or in East
Asia or in the Gulf
right so I believe in Primacy that's my
definition of Primacy to be the most
powerful state in the system but I'm not
interested to go back to my first point
in spreading liberal democracy again I
think liberal democracy is a wonderful
thing if every state in the world was a
liberal democracy I think that would be
good for the people who live in those
countries but my view is because I
believe in sovereignty it's up to them
to decide what they want
uh
final point I want to make to you here
on this slide is liberalism abroad leads
to illiberalism at home
this is what the founding fathers
understood if you're in a permanent
state of War
right it's going to have consequences
for liberalism at home because you're
going to create a National Security
State and you're going to have a state
that spies on people and does all sorts
of other things
so I think from a point of view of civil
liberties this foreign policy is
bankrupt final final point
the end of liberal hegemony remember
what John said to you very early in the
talk
I said that you could only have liberal
hegemony in unipolarity because in
unipolarity the soul pole which is the
United States does not have to worry
about great power politics because by
definition you can't have great power
politics when there's only one great
power
well we are now transitioning out of
unipolarity into multiple Clarity this
is a very clearly reflected in a
document on the country's National
Security strategy that the White House
issued in December of 2017 and then the
Pentagon in January of 2018
issued a similar document on our
national security strategy in both these
documents make it clear that
multi-polarity is here that unipolarity
is over with and great power politics is
what we're going to be mainly concerned
with in the future and that has to do
with one the rise of China which I think
for all of you young people in the
audience will be the most important
issue of your lifetime and then the
second issue is the resurrection of
Russian power after Putin came to office
in 2000 Russia is a declining great
power you don't want to overestimate
Russian power right China is the real
threat to the United States here but
nevertheless the Russians are back and
the Russians have thousands of nuclear
weapons and they can cause us a lot of
trouble and we are at loggerheads with
them over the Ukraine crisis so we want
to pay them serious attention but what
I'm saying to you here
is that I think with the coming
of multi-polarity liberal hegemony will
go away
now if I'm wrong and we remain in a
unipolar world because the Chinese rise
doesn't continue and Russia begins to
fall apart again and we are once again
the unipole then we're back to arguing
against
liberal hegemony and making the case for
restraint but I don't think that people
like me are going to have to make the
case for restraint in the future in
large part because of the rise of China
I would say this is my concluding point
that I have very mixed emotions about
that on one hand I welcome the rise of
China and the resurrection of Russian
power because it means that liberal
hegemony is going away
but on the other hand what it means is
that the United States is now facing a
potential peer competitor and I think
all things considered I'd rather have
liberal hegemony as a problem to deal
with rather than have China and Russia
as twin problems to deal with thank you
thank you
5.0 / 5 (30 votes)

スノーデン氏:監視社会巡りネット質疑

ブルームバーグ米国同盟国が米ドルに疑問。基軸通貨の地位が崩壊か。私の経験したバブル経済と崩壊。いまの状況との違いを解説。日本の景気回復の鍵は?消費促進には〇〇に金を渡せ。経済が疲弊しているのにバブルが
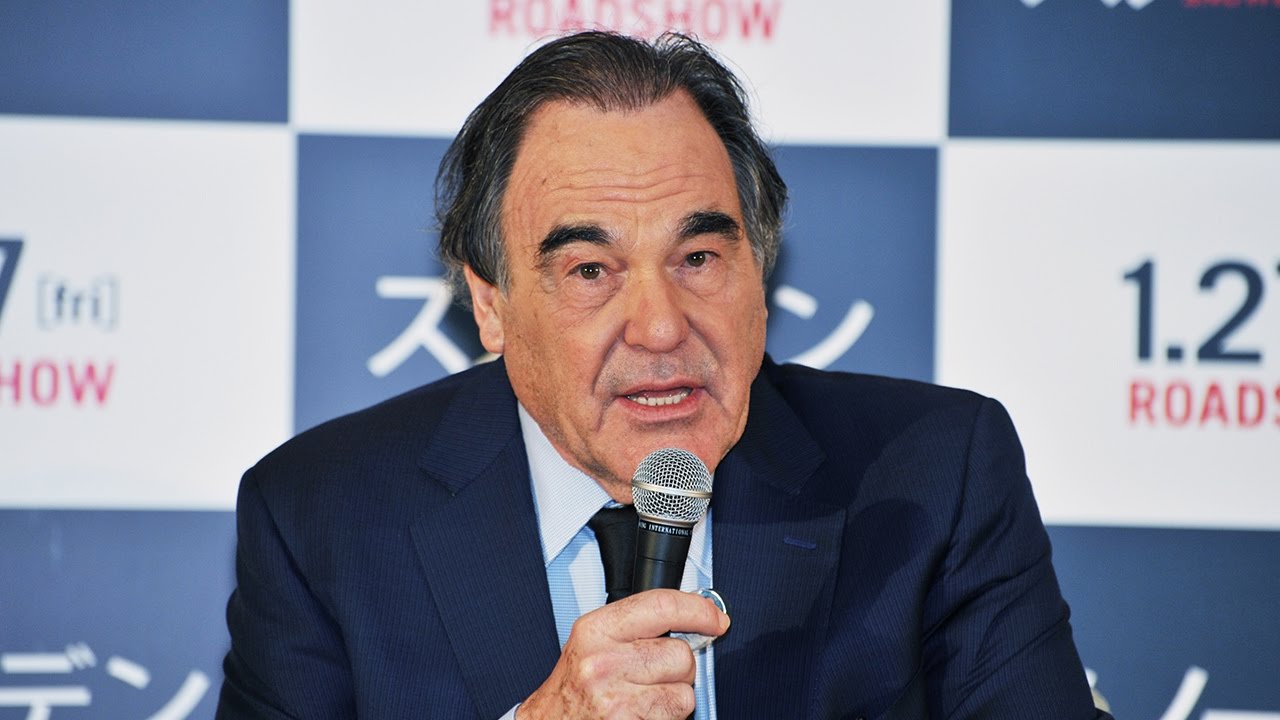

米国の同盟国をやめた瞬間に、CIAのマルウェアが日本中のインフラを崩壊させる!?スノーデン証言の真偽は⁉︎ーー映画『スノーデン』のオリバー・ストーン監督に岩上安身が直撃質問! 2017.1.18

Install macOS Sonoma BETA or Ventura 13.5 on UNSUPPORTED MACs with OpenCore Legacy Patcher 0.6.8!

【ダイジェスト】竹中平蔵が政界進出した理由と仕込まれたプロパカンダとは?(三橋貴明)

TERIYAKI BEEF / SEEDA & OKI (GEEK)